| 质粒类型: | 慢病毒载体 |
|---|---|
| 高拷贝/低拷贝: | 高拷贝 |
| 启动子: | EF1α/ EF1a |
| 克隆方法: | 多克隆位点,限制性内切酶 |
| 载体大小: | 8904 bp |
| 5' 测序引物及序列: | EF1a Forward: TCAAGCCTCAGACAGTGGTTC |
| 3' 测序引物及序列: | IRES-R: CCTCACATTGCCAAAAGACG |
| 载体抗性: | Ampicillin (氨苄青霉素) |
| 备注: | 载体能够表达mCherry荧光蛋白 |
| 产品编号 | 产品名称 | 规格 | 价格 |
|---|---|---|---|
| QC2013 | pLVX-EF1α-IRES-mCherry |
5ug质粒 |
¥1500.00 |
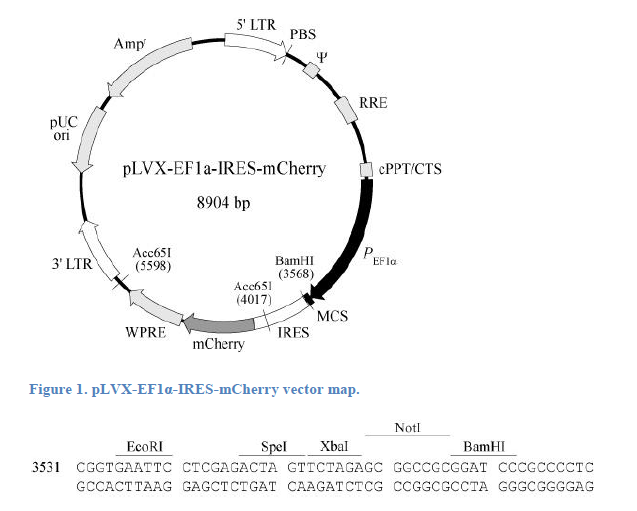
pLVX-EF1α-IRES-mCherry is an HIV-1-based, lentiviral expression vector designed to simultaneously and constitutively express a protein of interest and the green fluorescent protein mCherry from a bicistronic transcript in mammalian cells. mCherry is a mutant fluorescent protein derived from the tetrameric Discosoma sp. red fluorescent protein, DsRed (1). The excitation and emission maxima of the native mCherry protein are 587 nm and 610 nm, respectively.
Simultaneous expression of a protein of interest and mCherry is made possible by the presence of an encephalomyo-carditis virus internal ribosome entry site (IRES; 2) positioned between the multiple cloning site (MCS) and the mCherry gene. The IRES allows a protein of interest and mCherry to be translated from a single bicistronic mRNA. Stable, constitutive expression of the bicistronic transcript is driven by the EF1α promoter (PEF1α), which continues to be constitutively active even after vector integration into the host cell genome (3).
pLVX-EF1α-IRES-mCherry contains all of the viral processing elements necessary for the production of replication-incompetent lentivirus, as well as elements to improve viral titer, transgene expression, and overall vector function. The woodchuck hepatitis virus posttranscriptional regulatory element (WPRE) promotes RNA processing events and enhances nuclear export of viral RNA (4), leading to increased viral titers from packaging cells. In addition, the vector includes a Rev-response element (RRE), which further increases viral titers by enhancing the transport of unspliced viral RNA out of the nucleus (5). Finally, pLVX-EF1α-IRES-mCherry also contains a central polypurine tract/central termination sequence


